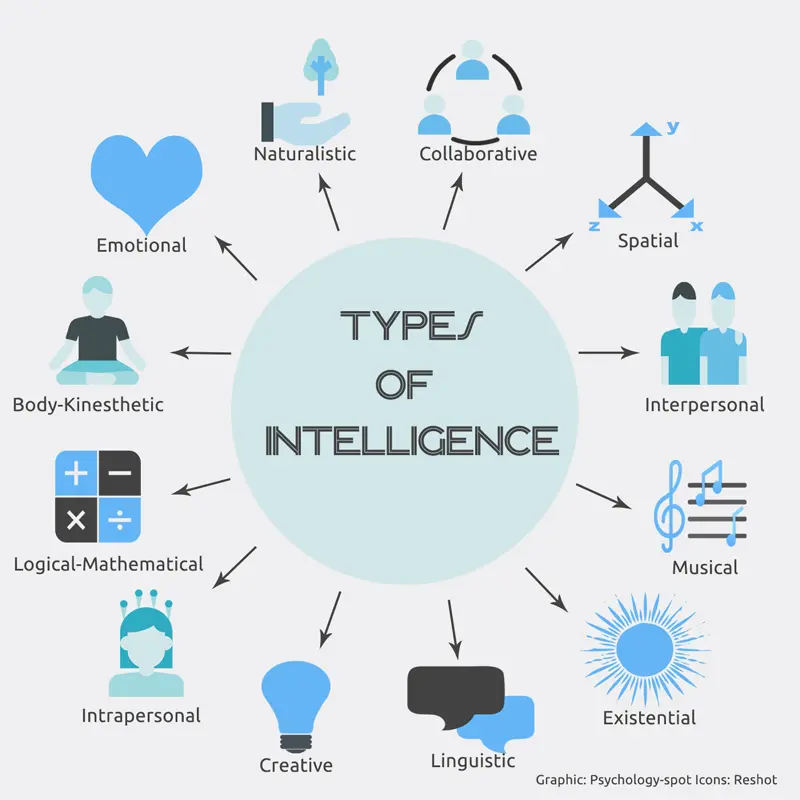
TYPE OF IQ
PHÂN LOẠI IQ
The concept of Intelligence Quotient (IQ) is often viewed through the lens of a single, general score that represents a person’s cognitive abilities relative to the population. However, intelligence is a multifaceted construct that encompasses various cognitive processes. The notion of different "types" of IQ reflects the diversity of intellectual abilities that contribute to an individual's overall cognitive profile. This essay explores the various types of IQ, delving into how different cognitive domains are measured, how they contribute to the broader understanding of intelligence, and their implications in educational and psychological contexts.
Khái niệm về Chỉ số thông minh (IQ) thường được xem xét thông qua lăng kính của một điểm số chung duy nhất đại diện cho khả năng nhận thức của một cá nhân so với dân số. Tuy nhiên, trí thông minh là một cấu trúc đa diện bao gồm nhiều quá trình nhận thức khác nhau. Khái niệm về các "loại" IQ khác nhau phản ánh sự đa dạng của các khả năng trí tuệ góp phần vào hồ sơ nhận thức tổng thể của một cá nhân. Có nhiều loại IQ khác nhau, phụ thuộc vào cách các lĩnh vực nhận thức khác nhau được đo lường, cách đóng góp vào sự hiểu biết rộng hơn về trí thông minh và ý nghĩa của mỗi loại IQ trong bối cảnh giáo dục và tâm lý.
Understanding General vs. Specific IQ
Hiểu General so với IQ cụ thể
The traditional view of IQ is based on the idea of a general intelligence factor, often referred to as "g." This concept, introduced by Charles Spearman in the early 20th century, suggests that a single underlying factor influences performance across various cognitive tasks. However, intelligence is not monolithic. Modern theories of intelligence, such as the Cattell-Horn-Carroll (CHC) theory, recognize multiple specific cognitive abilities that together make up a person’s overall IQ. These abilities are often categorized into different "types" of IQ, each representing distinct areas of cognitive functioning. .
Quan điểm truyền thống về IQ dựa trên ý tưởng về một yếu tố thông minh chung, thường được gọi là "g". Khái niệm này, được Charles Spearman giới thiệu vào đầu thế kỷ 20, cho rằng một yếu tố cơ bản duy nhất ảnh hưởng đến hiệu suất trong nhiều nhiệm vụ nhận thức khác nhau. Tuy nhiên, trí thông minh không phải là duy nhất. Các lý thuyết hiện đại về trí thông minh, chẳng hạn như lý thuyết Cattell-Horn-Carroll (CHC), công nhận nhiều khả năng nhận thức cụ thể cùng nhau tạo nên IQ tổng thể của một người. Những khả năng này thường được phân loại thành các "loại" IQ khác nhau, mỗi loại đại diện cho các lĩnh vực riêng biệt của chức năng nhận thức. .

Verbal IQ refers to a person’s ability to understand, analyze,
and express ideas through language. It includes skills such as
vocabulary, reading comprehension, verbal reasoning, and the
ability to communicate effectively. Verbal IQ is typically
measured through tasks that involve word definitions, similarities,
sentence comprehension, and analogies.
Verbal IQ is crucial for academic success,
particularly in subjects like literature, history,
and social studies. It also plays a significant role in
communication, problem-solving, and social interactions.
High verbal IQ is often associated with strong linguistic
abilities, while lower verbal IQ may indicate difficulties
with language-related tasks, which could impact academic
performance and social relationships.
IQ ngôn ngữ đề cập đến khả năng hiểu, phân tích và diễn đạt ý tưởng của một người thông qua ngôn ngữ.
Nó bao gồm các kỹ năng như vốn từ vựng, hiểu đọc, lý luận bằng lời và khả năng giao tiếp hiệu quả.
IQ ngôn ngữ thường được đo thông qua các nhiệm vụ liên quan đến định nghĩa từ, điểm tương đồng,
hiểu câu và phép loại suy.
IQ ngôn ngữ rất quan trọng đối với thành công trong học tập, đặc biệt là trong các môn học như văn học,
lịch sử và nghiên cứu xã hội. Nó cũng đóng vai trò quan trọng trong giao tiếp, giải quyết vấn đề và tương
tác xã hội. IQ ngôn ngữ cao thường gắn liền với khả năng ngôn ngữ mạnh mẽ, trong khi IQ ngôn ngữ thấp hơn
có thể chỉ ra những khó khăn trong các nhiệm vụ liên quan đến ngôn ngữ, điều này có thể ảnh hưởng đến thành
tích học tập và các mối quan hệ xã hội.
Performance IQ, also known as non-verbal IQ, measures an
individual’s ability to understand and solve problems without
relying on language. It includes skills such as spatial
reasoning, pattern recognition, visual-motor coordination, and
the ability to manipulate objects mentally. Performance IQ is
assessed through tasks that involve puzzles, block design, picture
completion, and matrix reasoning.
Performance IQ is particularly important in fields that require
strong visual-spatial skills, such as engineering, architecture,
and the visual arts. It also plays a role in everyday tasks that
require navigation, spatial awareness, and non-verbal problem-solving.
Individuals with high performance IQ often excel in tasks that involve
hands-on learning or visual-spatial reasoning.
IQ hiệu suất, còn được gọi là IQ phi ngôn ngữ, đo lường khả năng hiểu và
giải quyết vấn đề của một cá nhân mà không cần dựa vào ngôn ngữ.
Nó bao gồm các kỹ năng như lý luận không gian, nhận dạng mẫu,
phối hợp thị giác-vận động và khả năng thao tác các vật thể trong đầu.
IQ hiệu suất được đánh giá thông qua các nhiệm vụ liên quan đến câu đố, thiết kế khối,
hoàn thành hình ảnh và lý luận ma trận.
IQ hiệu suất đặc biệt quan trọng trong các lĩnh vực đòi hỏi kỹ năng thị giác-không gian mạnh mẽ,
chẳng hạn như kỹ thuật, kiếntrúc và nghệ thuật thị giác.
Nó cũng đóng một vai trò trong các nhiệm vụ hàng ngày đòi hỏi phải điều hướng,
nhận thức không gian và giải quyết vấn đề phi ngôn ngữ.
Những cá nhân có IQ hiệu suất cao thường xuất sắc trong các nhiệm vụ liên quan đến học tập
thực hành hoặc lý luận thị giác-không gian.

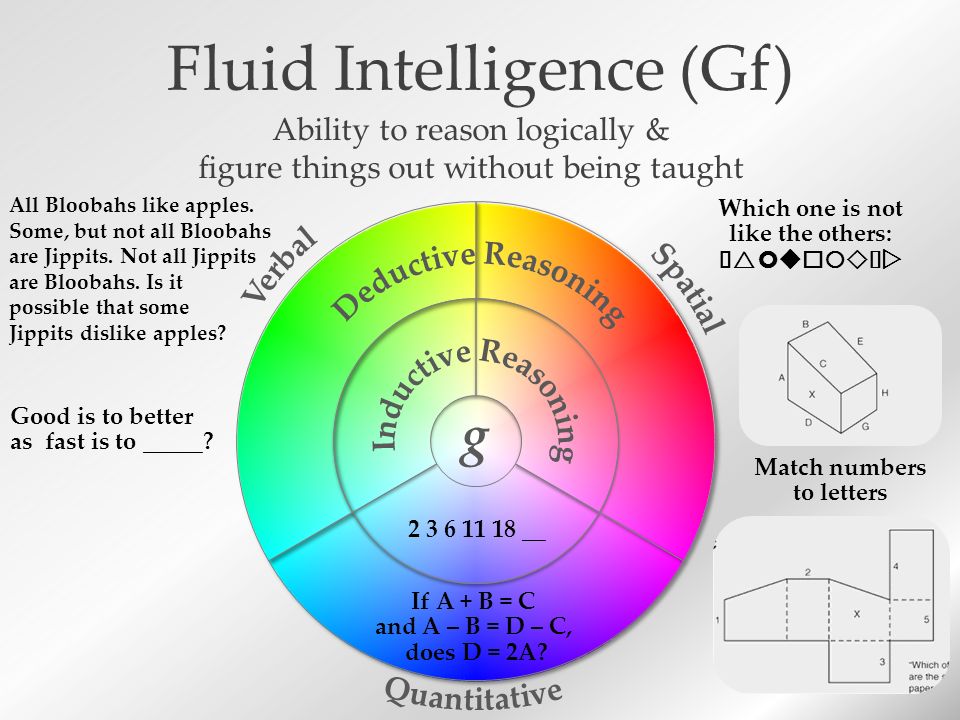
Fluid intelligence, or Gf, refers to the ability to solve new problems,
reason logically, and think abstractly in novel situations, independent
of acquired knowledge. It involves skills such as pattern recognition,
logical analysis, and the capacity to identify relationships among seemingly
unrelated elements. Fluid intelligence is often measured through tasks that
require solving puzzles, identifying sequences, and understanding complex patterns.
Fluid intelligence is essential for adaptive problem-solving and
the ability to learn new information quickly. It is particularly
relevant in fields that require innovation, critical thinking,
and the ability to tackle unfamiliar challenges. Fluid
intelligence tends to peak in early adulthood and gradually
declines with age, making it a focus of cognitive training
and enhancement strategies.
Trí thông minh lưu loát, đề cập đến khả năng giải quyết các vấn đề mới,
lý luận logic và suy nghĩ trừu tượng trong các tình huống mới lạ,
độc lập với kiến thức đã học. Nó bao gồm các kỹ năng như nhận dạng mẫu,
phân tích logic và khả năng xác định mối quan hệ giữa các yếu tố dường
như không liên quan. Trí thông minh lưu loát thường được đo lường thông
qua các nhiệm vụ đòi hỏi phải giải câu đố, xác định trình tự và hiểu các mẫu phức tạp.
Trí thông minh lưu loát rất cần thiết cho việc giải quyết vấn đề thích ứng
và khả năng học thông tin mới một cách nhanh chóng.
Nó đặc biệt có liên quan trong các lĩnh vực đòi hỏi sự đổi mới,
tư duy phản biện và khả năng giải quyết những thách thức không quen thuộc.
Trí thông minh lưu loát có xu hướng đạt đỉnh ở giai đoạn đầu tuổi trưởng thành và giảm dần theo tuổi tác,
khiến nó trở thành trọng tâm của các chiến lược đào tạo và nâng cao nhận thức.
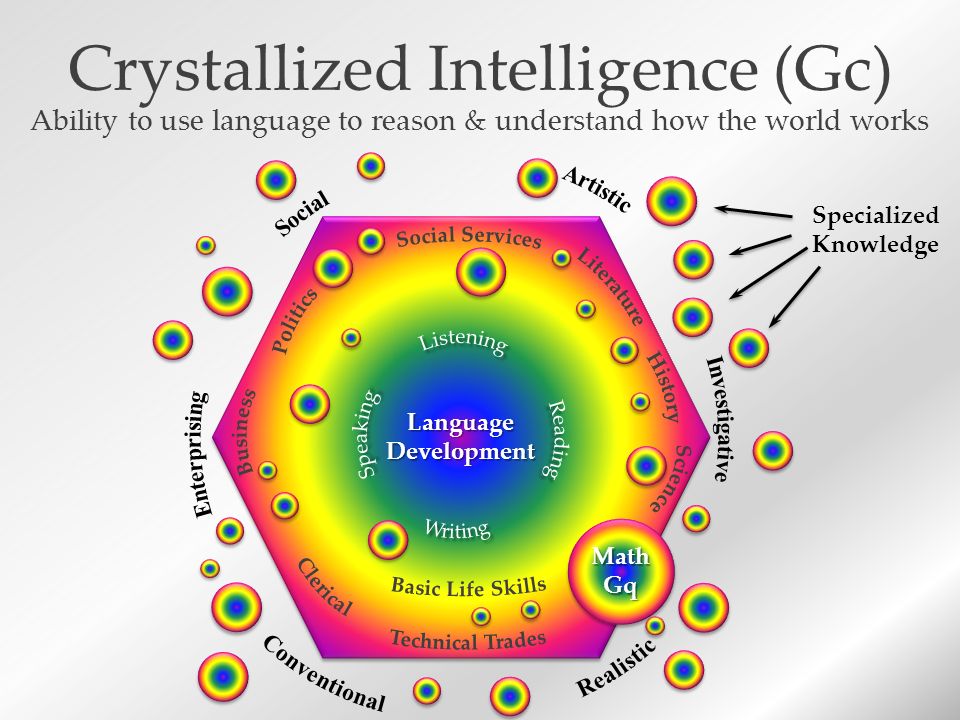
Crystallized intelligence, or Gc, encompasses the
knowledge and skills that individuals acquire over
their lifetime through education, experience, and
cultural exposure. It includes abilities such as
vocabulary, general knowledge, and understanding
of social norms and practices. Crystallized intelligence
is measured through tasks that assess factual knowledge,
reading comprehension, and the application of
learned information.
Crystallized intelligence tends to increase with age,
as individuals accumulate more knowledge and experience.
It is crucial for tasks that involve applying learned concepts,
making informed decisions, and understanding complex information.
Fields such as law, medicine, and academia often require high levels
of crystallized intelligence, as these professions depend on
the application of specialized knowledge.
Trí thông minh kết tinh bao gồm kiến thức và
kỹ năng mà cá nhân có được trong suốt cuộc
đời thông qua giáo dục, kinh nghiệm và tiếp
xúc văn hóa. Nó bao gồm các khả năng như vốn
từ vựng, kiến thức chung và hiểu biết về
các chuẩn mực và thông lệ xã hội. Trí thông minh
kết tinh được đo lường thông qua các nhiệm vụ
đánh giá kiến thức thực tế, khả năng
đọc hiểu và ứng dụng thông tin đã học.
Trí thông minh kết tinh có xu hướng tăng theo tuổi tác,
khi cá nhân tích lũy thêm kiến thức và kinh nghiệm.
Nó rất quan trọng đối với các nhiệm vụ liên quan đến
việc áp dụng các khái niệm đã học, đưa ra quyết định sáng
suốt và hiểu thông tin phức tạp. Các lĩnh vực như luật,
y học và học thuật thường đòi hỏi mức độ trí thông minh
kết tinh cao, vì những nghề này phụ thuộc vào việc áp dụng kiến
thức chuyên môn
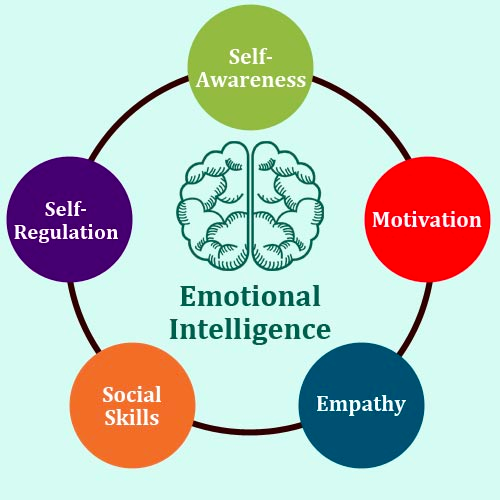
Emotional intelligence, or EQ, while not traditionally
included in IQ assessments, has gained recognition as an
important aspect of overall cognitive functioning.
EQ refers to the ability to recognize, understand,
and manage one’s own emotions, as well as the ability to
empathize with others and navigate social relationships effectively.
It includes skills such as emotional awareness, self-regulation, social
skills, and empathy.
Emotional intelligence is critical for personal well-being, leadership,
and interpersonal relationships. High EQ is associated with better mental
health, successful social interactions, and effective conflict resolution.
In educational and professional settings, individuals with high emotional
intelligence are often better equipped to handle stress, work collaboratively,
and lead teams effectively.
Trí tuệ cảm xúc, hay EQ, mặc dù không được đưa
vào đánh giá IQ theo truyền thống, đã được công
nhận là một khía cạnh quan trọng của chức năng
nhận thức tổng thể. EQ đề cập đến khả năng nhận biết,
hiểu và quản lý cảm xúc của chính mình, cũng như khả
năng đồng cảm với người khác và điều hướng các mối
quan hệ xã hội một cách hiệu quả. Nó bao gồm các kỹ
năng như nhận thức cảm xúc, tự điều chỉnh, kỹ năng
xã hội và sự đồng cảm.
Trí tuệ cảm xúc rất quan trọng đối với hạnh phúc cá nhân,
khả năng lãnh đạo và các mối quan hệ giữa các cá nhân.
EQ cao có liên quan đến sức khỏe tinh thần tốt hơn, các tương
tác xã hội thành công và giải quyết xung đột hiệu quả.
Trong môi trường giáo dục và nghề nghiệp, những cá nhân có
trí tuệ cảm xúc cao thường được trang bị tốt hơn để xử lý căng thẳng,
làm việc cộng tác và lãnh đạo nhóm hiệu quả.
Practical intelligence, sometimes referred to as "street smarts,"
involves the ability to solve real-world problems and adapt to changing
environments. It encompasses skills such as common sense, decision-making,
and the ability to apply knowledge in practical situations. Practical intelligence
is not typically measured by traditional IQ tests but is considered an important
aspect of overall intelligence.
Practical intelligence is crucial for success in everyday life,
particularly in situations that require quick thinking, resourcefulness,
and the ability to navigate social and practical challenges.
It is often associated with leadership, entrepreneurship, and
effective problem-solving in dynamic environments.
Trí thông minh thực tế, đôi khi được gọi là "trí thông minh môi trường",
bao gồm khả năng giải quyết các vấn đề thực tế và thích nghi với môi trường
thay đổi. Nó bao gồm các kỹ năng như ý thức chung, ra quyết định và khả năng
áp dụng kiến thức vào các tình huống thực tế. Trí thông minh thực tế
thường không được đo bằng các bài kiểm tra IQ truyền thống nhưng được coi
là một khía cạnh quan trọng của trí thông minh tổng thể.
Trí thông minh thực tế rất quan trọng để thành công trong cuộc sống hàng ngày,
đặc biệt là trong các tình huống đòi hỏi tư duy nhanh, tháo vát và khả năng điều
hướng các thách thức xã hội và thực tế. Nó thường gắn liền với khả năng lãnh đạo,
tinh thần kinh doanh và giải quyết vấn đề hiệu quả trong các môi trường năng động.

Implications of Different Types of IQ
Recognizing the different types of IQ has significant implications for education, psychology, and career development. It highlights the need for a more holistic approach to assessing and nurturing intelligence, one that goes beyond traditional IQ tests. In educational settings, understanding a student's unique cognitive profile can help tailor instruction and support to meet their specific needs. In psychology, a nuanced view of intelligence can inform more accurate diagnoses and interventions for cognitive and emotional challenges.
Moreover, in the workplace, acknowledging the diversity of cognitive abilities can lead to more effective team-building and leadership strategies. It can also help individuals identify their strengths and areas for development, guiding career choices and personal growth.
Conclusion.
The concept of IQ encompasses a wide range of cognitive abilities, each contributing to a person’s overall intellectual profile. By understanding the different types of IQ—such as verbal, performance, fluid, crystallized, emotional, and practical intelligence—we can gain a more comprehensive understanding of what it means to be intelligent. This multifaceted view of intelligence not only broadens our understanding of human potential but also informs more personalized and effective approaches to education, psychological assessment, and personal development. As our understanding of intelligence continues to evolve, it is important to recognize and value the diverse cognitive abilities that contribute to human success and well-being.
Tổng kết.
Khái niệm IQ bao gồm nhiều khả năng nhận thức, mỗi khả năng đều góp phần tạo sự đánh giá trí tuệ tổng thể của một cá nhân. Bằng cách hiểu các loại IQ khác nhau—chẳng hạn như trí thông minh ngôn ngữ, hiệu suất, lưu loát, kết tinh, cảm xúc và thực tế—chúng ta có thể hiểu toàn diện hơn về ý nghĩa của trí thông minh. Quan điểm đa diện này về trí thông minh không chỉ mở rộng hiểu biết của chúng ta về tiềm năng của con người mà còn cung cấp thông tin cho các phương pháp tiếp cận cá nhân hóa và hiệu quả hơn đối với giáo dục, đánh giá tâm lý và phát triển cá nhân. Khi hiểu biết của chúng ta về trí thông minh tiếp tục phát triển, điều quan trọng là phải nhận ra và đánh giá cao các khả năng nhận thức đa dạng góp phần vào thành công và hạnh phúc của con người.